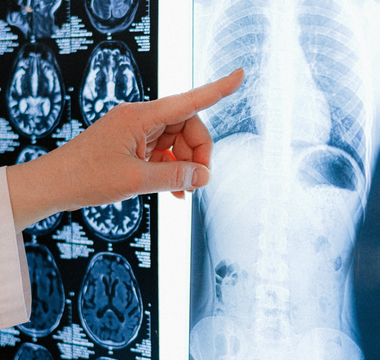
Medical imaging has revolutionized the field of healthcare, enabling physicians to visualize and diagnose a wide range of conditions. While imaging has traditionally been used for diagnostic purposes, there is a growing interest in the potential of preventive imaging to save lives by detecting and addressing health issues before they become critical. This article delves into the concept of preventive imaging, its impact on healthcare, and the potential benefits it holds for patients.
Understanding Preventive Imaging:
Preventive imaging, also known as screening or early detection imaging, involves the use of various medical imaging technologies to identify potential health problems in asymptomatic individuals. Unlike diagnostic imaging, which is employed when symptoms are present, preventive imaging aims to catch diseases at their earliest stages, often before symptoms manifest.
Common Preventive Imaging Modalities:
Several imaging modalities play a crucial role in preventive healthcare. Mammography, for example, is widely used for breast cancer screening, allowing the detection of abnormalities in breast tissue long before a patient experiences symptoms. Similarly, colonoscopies are employed for colorectal cancer screening, and various imaging techniques such as ultrasound and MRI can aid in early detection of conditions affecting organs like the heart, lungs, and liver.
Impact on Cancer Detection and Treatment:
One of the primary areas where preventive imaging has demonstrated significant impact is in the early detection of cancer. Many types of cancer, when detected at an early stage, are more treatable and have higher survival rates. Routine screenings, such as mammograms and Pap smears, have been instrumental in reducing mortality rates for breast and cervical cancers. Advances in imaging technologies continue to improve the accuracy and efficiency of cancer screening, offering hope for better outcomes in the fight against this deadly disease.
Cardiovascular Health and Preventive Imaging:
Beyond cancer, preventive imaging plays a vital role in assessing cardiovascular health. Non-invasive imaging techniques, such as CT angiography and calcium scoring, can identify early signs of heart disease, enabling intervention before a cardiac event occurs. Timely detection of conditions like atherosclerosis or aneurysms can lead to preventive measures, such as lifestyle changes or medical treatments, that reduce the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Challenges and Considerations:
While preventive imaging holds great promise, it is not without challenges. False positives can lead to unnecessary stress and invasive follow-up procedures, while false negatives may provide a false sense of security. Additionally, there are concerns about radiation exposure in certain imaging techniques, prompting ongoing research into safer alternatives.
Cost-effectiveness is another consideration, as widespread screening programs can strain healthcare budgets. Striking the right balance between cost and benefit is crucial for the sustainable implementation of preventive imaging strategies.
Conclusion:
Preventive imaging has the potential to revolutionize healthcare by saving lives through early detection and intervention. As technology advances and our understanding of various diseases deepens, the role of imaging in preventive medicine will likely continue to expand. It is essential for healthcare providers, policymakers, and researchers to work collaboratively in addressing challenges, ensuring accessibility, and refining protocols to maximize the benefits of preventive imaging for individuals and society as a whole. As we navigate the future of healthcare, preventive imaging stands as a powerful tool in the ongoing quest to improve patient outcomes and save lives.
Cart 0
Your cart is currently empty.
Start Shopping
Trending Now